By Harpreet Singh Wasu
There are two types of permissions that you can give to a service account for GAL or Public Folder Sync to User Mailboxes.
The first way you can give the permissions is by Delegation and second is by Impersonation.
This Blog Post shows how to setup the Service Account for Impersonation mode in Office 365 (Exchange Online).
If you are looking to find the steps to give the permissions using mailbox Delegation, navigate to Exchange Service Account Permissions and itrezzo Contact Management
If you would like to enable App Impersonation via PowerShell, read the blog post How to Configure an Office 365 Hybrid Premise Service Account.
You can also refer to the Microsoft Article on How to Configure Application Impersonation using PowerShell.
There are two types of permissions that you can give to a service account for GAL or Public Folder Sync to User Mailboxes.
The first way you can give the permissions is by Delegation and second is by Impersonation.
This Blog Post shows how to setup the Service Account for Impersonation mode in Office 365 (Exchange Online).
If your organization is Cloud-Only (All mailboxes are in Office 365) you should use the below steps to grant Application Impersonation role to your mailbox.
If you are looking to find the steps to give the permissions using mailbox Delegation, navigate to Exchange Service Account Permissions and itrezzo Contact Management
How to setup App Impersonation for Office 365 and Exchange 2013/2016
1. Log in to your Office 365 portal as a Global Administrator and Navigate to Office 365 Admin Center by clicking on Admin.

2. From the Office 365 Admin Center, expand the navigation bar on the left side and scroll to the bottom and expand Admin and then click on Exchange. You can also navigate to Exchange Admin Centre (EAC) through https://outlook.office365.com/ecp/
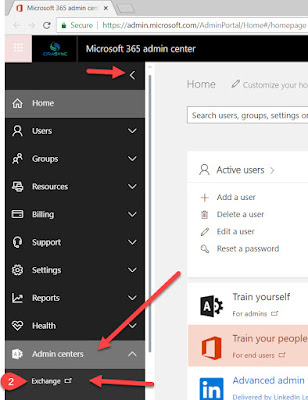
3. From the EAC, either Click on Permissions on the left-hand navigation and make sure you are under Admin Roles Tab at the top or Click on Admin Roles below Permissions on the Home page of EAC
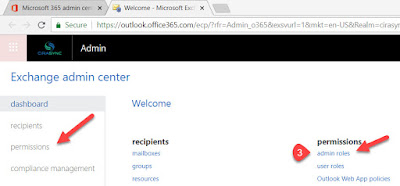
4. Check if you already have a Role Group created with Application Impersonation Role. If not, create a New Role Group by clicking on the + sign.
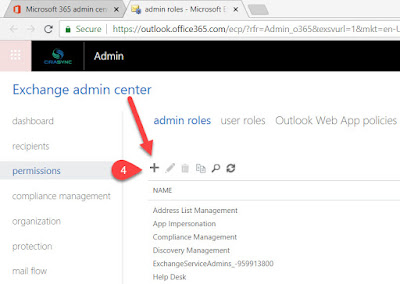
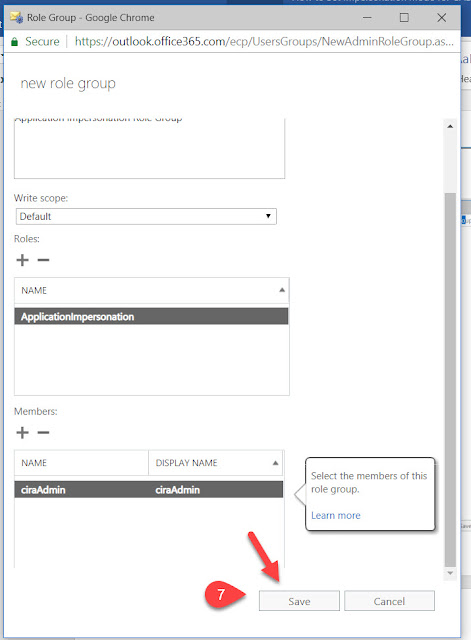
5. In the New Role Group window, give a name for this New Role Group. For easy to remember, you can name is App Impersonation. Give any description of your choice in the Description Box. Click + on Roles. Select Application Impersonation and Click Add and OK.
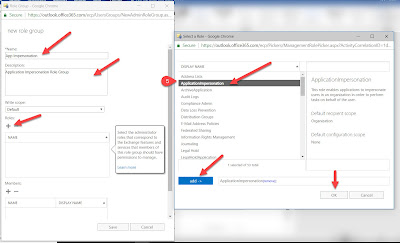
6. Now Click on + sign below the Members, add the Service Account as the Member of this Role Group, click on Add and OK.
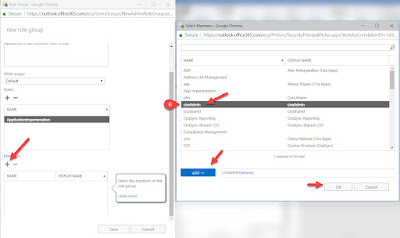
7. Once it’s done, click on Save in the New Role Group Window.

2. From the Office 365 Admin Center, expand the navigation bar on the left side and scroll to the bottom and expand Admin and then click on Exchange. You can also navigate to Exchange Admin Centre (EAC) through https://outlook.office365.com/ecp/

3. From the EAC, either Click on Permissions on the left-hand navigation and make sure you are under Admin Roles Tab at the top or Click on Admin Roles below Permissions on the Home page of EAC

4. Check if you already have a Role Group created with Application Impersonation Role. If not, create a New Role Group by clicking on the + sign.

5. In the New Role Group window, give a name for this New Role Group. For easy to remember, you can name is App Impersonation. Give any description of your choice in the Description Box. Click + on Roles. Select Application Impersonation and Click Add and OK.

6. Now Click on + sign below the Members, add the Service Account as the Member of this Role Group, click on Add and OK.

7. Once it’s done, click on Save in the New Role Group Window.

It can sometimes take several minutes (generally 30-60 minutes) or these changes to become active and get replicated across all the directories.
If you would like to enable App Impersonation via PowerShell, read the blog post How to Configure an Office 365 Hybrid Premise Service Account.
Want to Learn how and when to use impersonation in your Exchange Server or Exchange Online environment, check out Impersonation and EWS in Exchange
You can also refer to the Microsoft Article on How to Configure Application Impersonation using PowerShell.